The landscape for hex head bolts is evolving. A custom fasteners manufacturer now considers advanced materials beyond traditional bolt casting. This shift impacts every hex bolt and custom fasteners application. The premier materials for 2026 reflect this progress.
The top 10 materials include:
- Carbon Steel (Grades 2, 5, 8)
- Stainless Steel (304, 316)
- Alloy Steel (4140, 4340)
- Titanium Alloys (Grade 5)
- Nickel Alloys (Inconel, Monel)
- Super Duplex Stainless Steel
- Aluminum Alloys (7075)
- Silicon Bronze
- Polymer Composites (PEEK)
- Graphene-Coated Steels
1. Carbon Steel for Hex Head Bolts (Grades 2, 5, 8)

Carbon steel remains the foundational material for fasteners in 2026. Its enduring popularity stems from a reliable combination of strength, cost, and versatility. Manufacturers produce these bolts in vast quantities, making them a go-to choice for countless industries. The material’s properties are well-defined by established standards, ensuring consistent performance and safety across applications.
Key Properties
High Tensile Strength
Carbon steel provides excellent tensile strength, which is the ability to resist being pulled apart. This strength is crucial for creating secure and durable joints. The heat treatment process further enhances this property, especially in higher grades, allowing the bolts to handle significant loads without failing.
Cost-Effectiveness
This material offers an exceptional balance of performance and price. The raw materials are abundant, and the manufacturing processes are highly optimized. This economic advantage makes carbon steel hex head bolts the most practical option for large-scale projects where budget is a primary consideration.
Wide Availability
Engineers and builders can source carbon steel fasteners from a global network of suppliers. This widespread availability simplifies logistics and procurement, preventing project delays. Whether for a small repair or a massive infrastructure project, the right carbon steel bolt is almost always readily accessible.
Grade-Specific Strength
Carbon steel is not a one-size-fits-all material. Specific grades, defined by standards like SAE J429, offer distinct levels of strength. This allows engineers to select the precise fastener for the job.
| Standard | Grade/Class | Material Type | Tensile Strength (psi) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAE J429 | Grade 2 | Low or Medium Carbon Steel | 74,000 (≤ 3/4″) |
| SAE J429 | Grade 5 | Medium Carbon Steel, Quenched & Tempered | 120,000 (≤ 1″) |
| SAE J429 | Grade 8 | Medium Carbon Alloy Steel, Quenched & Tempered | 150,000 (≤ 1-1/2″) |
| ISO R898 | Class 8.8 | Alloy Steel, Quenched & Tempered | 120,000 |
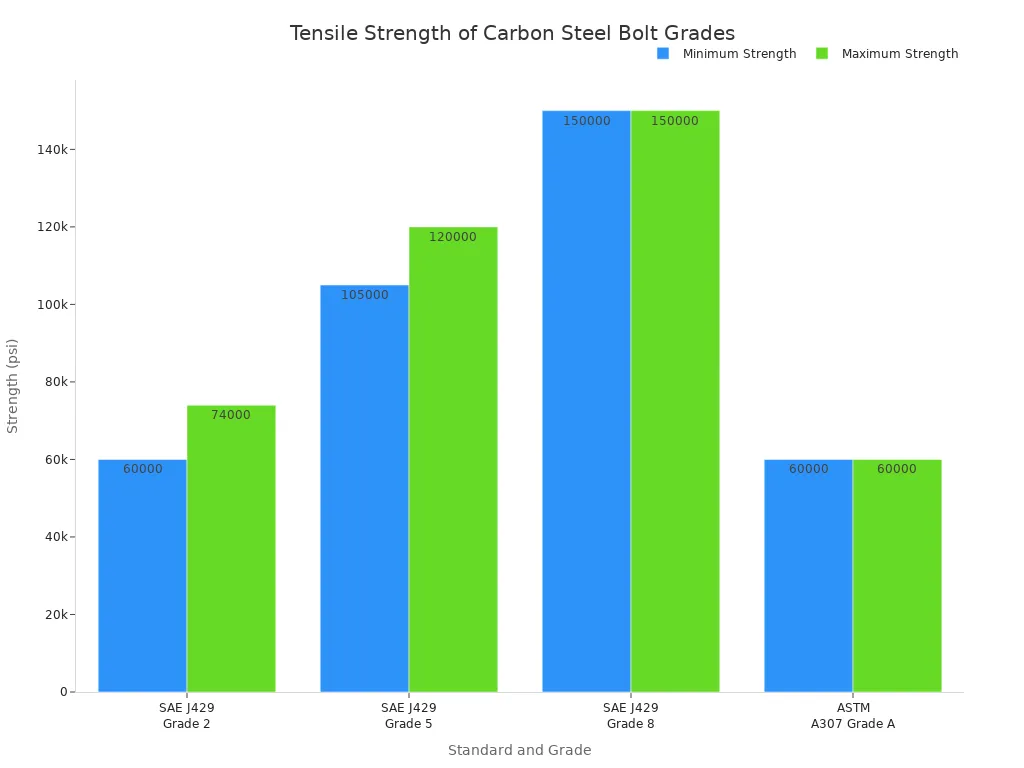
Pro Tip: Always match the grade to the application’s load requirements. Using a lower-grade bolt like Grade 2 in a high-stress environment designed for Grade 8 can lead to catastrophic failure.
Primary 2026 Applications
General Construction
Rapid urban expansion continues to drive demand for carbon steel bolts. They are essential for erecting building frames, assembling bridges, and constructing transportation networks where reliable strength is paramount.
Automotive Assembly
The automotive industry relies heavily on carbon steel fasteners. Increased industrial automation and smart manufacturing processes demand high-strength, dependable bolts for vehicle frames, engine mounts, and suspension systems.
Machinery Manufacturing
Heavy machinery and industrial equipment require robust fasteners that can withstand constant vibration and high loads. Carbon steel bolts provide the necessary strength and durability for assembling everything from factory conveyors to agricultural combines.
Consumer Products
From home appliances to furniture and exercise equipment, low- and medium-strength carbon steel bolts offer a cost-effective and reliable solution for assembling everyday items.
2. Stainless Steel Hex Head Bolts (304, 316)

Stainless steel represents a significant upgrade from carbon steel, especially in environments where corrosion is a major concern. In 2026, its use continues to expand as industries demand longer-lasting components with minimal maintenance. The two most prominent grades, 304 and 316, offer distinct advantages for specific, demanding applications. These materials provide a powerful combination of performance, longevity, and visual appeal.
Key Properties
Excellent Corrosion Resistance
The defining feature of stainless steel is its ability to resist rust and corrosion. This property comes from its chromium content, which forms a passive, self-repairing oxide layer on the surface. While both common grades are effective, their performance varies significantly in corrosive environments. Grade 316, with its added molybdenum, offers superior protection against chlorides, making it the preferred choice for marine-grade applications.
| Feature | 304 Stainless Steel | 316 Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Contains approximately 18% chromium and 8-10% nickel. | Contains 2-3% molybdenum in addition to iron, chromium, and nickel. |
| Corrosion in Marine Environments | More susceptible to pitting corrosion when exposed to chlorides. | Significantly enhanced resistance to chloride-induced corrosion, making it marine-grade. |
| Suitability for Marine Use | Less suitable for direct saltwater exposure. | Superior choice for most marine applications, especially those involving saltwater. |
Laboratory salt spray tests, like ASTM B117, consistently confirm that 316 stainless steel shows far less corrosion than 304, reinforcing its status for harsh maritime conditions.
Good Strength and Durability
Stainless steel hex head bolts provide reliable strength and excellent durability. While they may not match the sheer tensile strength of quenched and tempered alloy steels, they offer a robust solution for applications that require both mechanical integrity and environmental resistance. This balance makes them highly versatile.
Aesthetic Appeal
These fasteners possess a clean, bright finish that does not require a protective coating. This inherent aesthetic quality makes them ideal for architectural elements, consumer products, and any application where the bolts are visible and contribute to the overall design.
Hygienic Surface
Stainless steel has a non-porous surface that resists bacterial growth and is easy to clean and sterilize. This characteristic is non-negotiable in industries with strict sanitation standards, ensuring safety and compliance.
Primary 2026 Applications
Marine Equipment
Grade 316 is the standard for boat building and offshore structures. It secures everything from railings and deck hardware to engine components that are constantly exposed to saltwater spray and immersion.
Food Processing Machinery
The hygienic properties and resistance to corrosive cleaning agents make stainless steel essential for the food and beverage industry. It ensures that equipment remains sanitary and does not contaminate products.
Medical Devices
From hospital equipment to surgical tools, stainless steel’s ability to withstand repeated sterilization cycles makes it a critical material. Its biocompatibility is also a key factor in many medical applications.
Architectural Fixtures
Designers and architects specify stainless steel bolts for glass facades, balustrades, and outdoor sculptures. They choose them for their modern look and their ability to withstand weathering without rusting or staining adjacent materials.
3. Alloy Steel (4140, 4340)
When applications demand strength beyond standard carbon steel, engineers turn to alloy steel. By adding elements like chromium, molybdenum, and nickel, manufacturers create fasteners with exceptional mechanical properties. In 2026, chromium-molybdenum steels like 4140 and 4340 are indispensable for high-stress, high-performance environments where failure is not an option. These materials provide a significant leap in strength and durability, making them a cornerstone of advanced engineering.
Key Properties
Superior Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Alloy steels deliver immense strength without a proportional increase in weight. This characteristic is vital for applications where both power and efficiency are critical. Heat-treated alloy steel bolts can handle extreme loads that would deform or break carbon steel fasteners of the same size. The addition of specific alloying elements directly contributes to this enhanced performance.
| Property | 4140 Steel (Quenched & Tempered) | 4340 Steel (Quenched & Tempered) |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 850 – 1000 MPa | 930 – 1080 MPa |
| Yield Strength | 680 – 900 MPa | 740 – 1000 MPa |
| Hardness | 20 – 25 HRC | 22 – 28 HRC |
Excellent Toughness
Toughness is a material’s ability to absorb energy and resist fracturing under impact. Alloy steels, particularly the nickel-containing 4340 grade, exhibit outstanding toughness. This resilience makes them ideal for applications involving sudden shocks or heavy dynamic loads, ensuring the fastener bends before it breaks.
High Fatigue Resistance
Many mechanical systems expose bolts to constant vibration and cyclical loading. Alloy steels possess high fatigue resistance, allowing them to endure these repeated stresses over long periods without failing. This long-term reliability is crucial for the safety and longevity of critical machinery and structures.
Heat Treatment Response
The true potential of alloy steel is unlocked through heat treatment. Processes like quenching and tempering transform the steel’s internal microstructure into fine-grained tempered martensite. This structural change dramatically increases hardness and tensile strength.
Note: The mechanical properties of 4140 and 4340 steels are highly dependent on the heat treatment process. Proper quenching and tempering are not just enhancements; they are essential steps to achieve the high-strength characteristics for which these alloys are specified.
Primary 2026 Applications
Oil & Gas Sector
The oil and gas industry operates under extreme conditions. Equipment faces immense pressures, high temperatures, and corrosive substances like hydrogen sulfide. Alloy steel bolts provide the robust strength and resilience needed to secure critical connections on pipeline flanges, pressure vessels, and blowout preventers, ensuring operational safety and preventing catastrophic leaks.
Aerospace Engine Components
Jet engines and turbines require fasteners that can withstand intense heat and vibrational forces. The high strength and temperature stability of alloy steel make it a perfect fit for securing engine casings and internal components.
Heavy-Duty Industrial Equipment
In sectors like mining, manufacturing, and construction, heavy machinery endures constant punishment. Alloy steel hex head bolts provide the necessary clamping force and fatigue resistance to hold together excavators, presses, and large-scale compressors.
High-Performance Automotive
The world of motorsport and high-performance vehicles demands maximum strength with minimal weight. Engineers use alloy steel bolts in critical areas like engine assemblies, suspension systems, and chassis components to ensure reliability under extreme racing conditions.
4. Titanium Alloys (Grade 5 – Ti-6Al-4V)
Titanium alloys occupy the premium tier of fastener materials. Grade 5 titanium, also known as Ti-6Al-4V, is the most common alloy. It offers a combination of properties that are simply unattainable with steel or aluminum. In 2026, its use is critical in industries where performance is the absolute priority and cost is a secondary concern. This material represents the pinnacle of lightweight strength and environmental resilience.
Key Properties
Exceptional Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Titanium’s most celebrated feature is its incredible strength relative to its low density. A titanium bolt can provide the same strength as a steel bolt at roughly half the weight. This characteristic is a game-changer in applications where every gram matters. A direct comparison with other high-strength metals clearly illustrates its superior efficiency.

While high-performance aluminum is comparable, titanium maintains its strength advantage at much higher temperatures.
Outstanding Corrosion Resistance
Titanium forms a highly stable, passive, and self-healing oxide layer on its surface. This layer makes it virtually immune to corrosion from saltwater, chlorides, and a wide range of industrial acids. Its resistance far exceeds that of even marine-grade 316 stainless steel, ensuring extreme longevity in the harshest chemical and marine environments.
High-Temperature Stability
This material performs exceptionally well at elevated temperatures. Titanium alloys retain their strength and structural integrity at temperatures that would cause aluminum alloys to weaken significantly. This stability makes them essential for components operating in or near high-heat sources like engines and exhaust systems.
Biocompatibility
Titanium is non-toxic and not rejected by the human body. This unique property makes it the gold standard for medical devices that come into direct contact with bone and tissue. Its suitability is formally recognized by stringent industry standards.
Medical-Grade Certification ⚕️ The biocompatibility of Grade 5 titanium is specified for surgical implant applications under standards like:
- ASTM F136: This standard defines the chemical, mechanical, and metallurgical requirements for wrought Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Extra Low Interstitials) alloy for use in the manufacture of surgical implants.
Primary 2026 Applications
Aerospace and Defense Systems
Engineers use titanium bolts extensively in aircraft frames, landing gear, and engine mounts. The material’s high strength and low weight contribute directly to improved fuel efficiency and greater payload capacity in both commercial and military aircraft.
High-Performance Racing
In elite motorsports like Formula 1 and MotoGP, teams use titanium fasteners to reduce vehicle weight, lower the center of gravity, and increase speed. They are found in engines, chassis, and suspension components where performance gains are measured in milliseconds.
Advanced Medical Implants
The biocompatibility and strength of titanium make it the premier material for orthopedic implants like hip and knee joints, dental implants, and bone-fixing screws and plates.
Chemical Processing
Chemical plants use titanium hex head bolts to secure equipment that handles highly corrosive substances. They provide long-term, maintenance-free service in environments where other metals would quickly fail.
5. Nickel Alloys for Hex Head Bolts (Inconel, Monel)
Nickel alloys represent the elite class of fastener materials, engineered for service in the most punishing environments on Earth. When conditions involving extreme heat, aggressive chemicals, and immense pressure cause other metals to fail, alloys like Inconel and Monel provide unparalleled reliability. Their specialized compositions make them essential for industries where safety and performance are non-negotiable.
Key Properties
Extreme Temperature Resistance
Nickel alloys exhibit remarkable strength across a vast temperature spectrum, from cryogenic lows to searing highs. Inconel 718, for example, maintains exceptional creep rupture strength at temperatures up to 1300°F (700°C). It can also withstand intermittent service in environments reaching 1800°F (982°C), making it a critical material for high-temperature machinery.
Superior Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
These alloys provide robust defense against a wide range of corrosive media. Monel shows excellent performance against chemicals like sulfuric and hydrochloric acids. Inconel 625 also offers outstanding resistance, particularly in applications involving both chemical exposure and high heat. The specific alloying elements determine each material’s ideal use case.
| Alloy | Key Composition Elements | Performance in Acidic Environments |
|---|---|---|
| Monel 400 | High copper | Lacks significant chromium or molybdenum for oxidizing or acidic environments |
| Inconel 625 | Nickel, chromium, molybdenum | Suitable for corrosive conditions |
| Hastelloy C-276 | High molybdenum, chromium | Excels in reducing acid environments like sulfuric or hydrochloric systems |
High Mechanical Strength
Nickel alloys deliver impressive mechanical strength, often comparable to heat-treated alloy steels. Their key advantage is the ability to retain this strength under conditions that would severely weaken other materials. This ensures that bolted joints remain secure and stable despite extreme operational stresses.
Resistance to Oxidation
The high nickel and chromium content in these alloys promotes the formation of a durable, passive oxide layer on the fastener’s surface. This layer protects the underlying metal from oxidation and scaling at elevated temperatures, ensuring a long and predictable service life.
Primary 2026 Applications
Chemical Processing Plants
Engineers specify nickel alloy fasteners for reactors, piping systems, and heat exchangers that handle highly corrosive substances. Their ability to resist chemical attack prevents equipment failure and maintains operational safety.
Jet Engines and Gas Turbines
The aerospace industry relies on nickel alloys for critical components inside jet engines and gas turbines. These fasteners secure parts exposed to intense heat and vibrational forces, from turbine blades to afterburner sections.
Nuclear Reactors
Safety in nuclear power generation is paramount. Nickel alloy bolts are essential for their ability to withstand extreme heat, intense radiation, and corrosion from cooling systems. These fasteners must meet strict regulatory standards, including:
- Complete traceability of raw materials.
- Rigorous testing to verify mechanical properties.
- Compliance with codes like ASME and ASTM.
Subsea Equipment
For offshore oil and gas operations, nickel alloys provide the high-integrity bolting needed to withstand harsh marine environments. These hex head bolts secure subsea wellheads, pipeline flanges, and down-hole equipment, offering superior resistance to saltwater corrosion and immense pressures.
6. Super Duplex Stainless Steel
Super Duplex Stainless Steel (SDSS) offers a superior combination of strength and corrosion resistance. It effectively bridges the gap between standard stainless steels and high-cost nickel alloys. In 2026, engineers specify this material for critical applications where both mechanical performance and environmental durability are essential. Its balanced microstructure provides a unique set of properties that solve complex engineering challenges in harsh environments.
Key Properties
Resistance to Chloride Stress Corrosion Cracking
Standard austenitic stainless steels can fail under tension in chloride-rich environments. Super Duplex, however, provides outstanding resistance to this phenomenon, known as chloride stress corrosion cracking (SCC). This makes it a highly reliable choice for fasteners used in marine and chemical processing industries, ensuring long-term structural integrity.
High Tensile and Yield Strength
Super Duplex demonstrates exceptional mechanical properties. Its yield strength is more than double that of common austenitic stainless steels like 316L. This enhanced strength allows designers to use thinner, lighter fasteners and components without sacrificing performance. The result is a potential for significant material and cost savings in large-scale projects.
Excellent Pitting and Crevice Corrosion Resistance
This material excels at resisting localized corrosion. Its performance is often measured by the Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number (PREN). Materials with a PREN value greater than 40 are considered suitable for direct seawater service. Super Duplex grades consistently meet this high standard.
| STEEL TYPE | PREN |
|---|---|
| SAF 2507 | > 40 |
| Zeron 100 | > 40 |
| Ferrinox 255 | > 40 |
Dual Austenitic-Ferritic Microstructure
The defining characteristic of Super Duplex is its balanced, two-phase microstructure, containing roughly equal parts austenite and ferrite. This biphasic structure combines the toughness and corrosion resistance of austenitic steel with the high strength of ferritic steel. During deformation, strain transfers from the stronger ferrite phase to the more ductile austenite phase, contributing to the material’s overall superior strength and hardness.
Primary 2026 Applications
Desalination Plants
Desalination facilities expose equipment to high-pressure, highly corrosive seawater. Super Duplex hex head bolts provide the necessary strength and corrosion resistance for pumps, piping flanges, and filtration systems, ensuring operational reliability and preventing costly failures.
Offshore Oil Rigs
Challenge Solved Offshore platforms face extreme pressures, corrosive seawater, and harsh chemicals. Super Duplex bolts provide the high strength and superior corrosion resistance needed to secure critical equipment, reducing downtime and enhancing operational safety.
Chemical Tankers
Vessels transporting aggressive chemicals require fasteners that can withstand constant corrosive attack. Super Duplex bolts offer the robust chemical resistance needed to maintain the integrity of tanks and piping systems, preventing dangerous leaks.
Pulp and Paper Industry
The pulp and paper manufacturing process uses bleaching agents and other corrosive chemicals. Super Duplex fasteners provide the durability required for equipment like digesters and bleaching towers, extending service life and minimizing maintenance.
7. Aluminum Alloys (7075)
Aluminum alloys, particularly the high-strength 7075 grade, provide an essential lightweight alternative to traditional steels. In 2026, industries focused on mobility and efficiency increasingly rely on this material. Its primary alloying elements—zinc, magnesium, and copper—give it strength properties comparable to many steels but at a fraction of the weight. This makes 7075 aluminum hex head bolts a strategic choice for advanced engineering applications where mass is a critical design parameter.
Key Properties
Extremely Lightweight
The most significant advantage of aluminum is its low density. Aluminum’s density is approximately one-third that of steel. This means an aluminum 7075 bolt offers a weight reduction of around 66% compared to a steel bolt of the same dimensions. This dramatic weight saving is a game-changer for applications where minimizing mass is the top priority.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
While lightweight, 7075 aluminum does not compromise on strength. The T6 temper, achieved through heat treatment, gives the alloy impressive mechanical properties. This allows engineers to design strong, reliable joints without the weight penalty of steel, making it one of the best materials on a strength-to-weight basis.
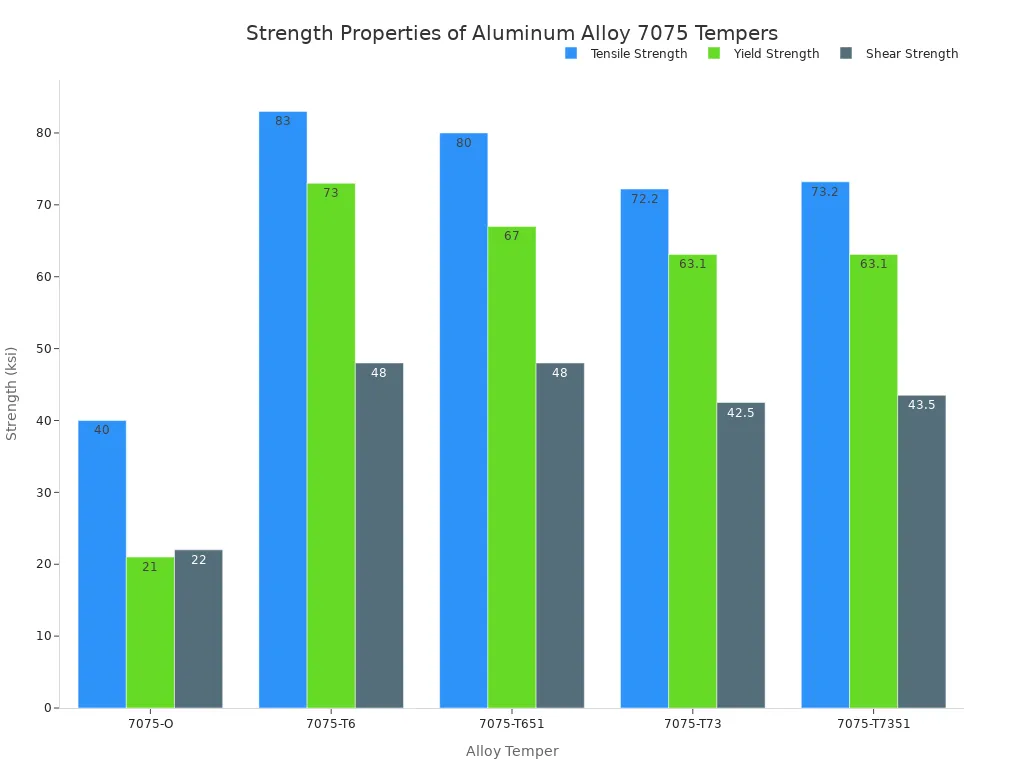
| Property | 7075-T6 | 7075-T651 |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (ksi) | 83 | 80 |
| Yield Strength (ksi) | 73 | 67 |
| Shear Strength (ksi) | 48 | 48 |
| Density (lb/in³) | 0.1 | 0.1 |
Non-Magnetic
Aluminum 7075 is completely non-magnetic. This property is essential for fasteners used in or near sensitive electronic equipment, such as advanced sensor arrays or medical imaging devices. Using non-magnetic bolts prevents electromagnetic interference, ensuring the accurate performance of the surrounding components.
Good Machinability
Manufacturers rate 7075 aluminum as having “fair” machinability, especially when compared to the “good” rating of the 6061 alloy. However, many machinists appreciate its characteristics. Because it is harder and less “gummy” than other alloys, it produces consistent, well-formed chips and is less likely to deform during the machining process.
Primary 2026 Applications
Drones and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
Performance Boost ✈️ For drones, every gram counts. Using lightweight 7075 aluminum bolts reduces overall vehicle mass, directly translating to longer flight times, increased payload capacity, and enhanced maneuverability.
Lightweight Robotics
In modern robotics, speed and energy efficiency are key. Aluminum 7075 fasteners help reduce the inertial mass of robotic arms and mobile platforms. This allows for faster acceleration and deceleration, enabling robots to perform tasks more quickly while consuming less power.
Aerospace Interior Structures
Engineers use 7075 aluminum bolts extensively inside aircraft cabins. They secure components like seat frames, overhead storage bins, and galley structures. Here, the material’s high strength-to-weight ratio contributes to reducing the aircraft’s overall weight, which improves fuel efficiency.
Performance Sporting Goods
High-end sporting equipment demands maximum performance. Manufacturers use 7075 aluminum bolts in products like competitive cycling components, rock climbing gear, and performance racing parts. Athletes benefit from the reduced weight without sacrificing the strength and safety needed for competition.
8. Silicon Bronze
Silicon Bronze carves out a unique niche in the fastener market, blending classic aesthetics with robust performance. This copper-based alloy, primarily containing silicon and sometimes zinc, offers a distinct set of properties. Engineers in 2026 choose it for applications where both environmental resilience and visual appeal are paramount. It stands as a premier choice for challenging marine and electrical applications.
Key Properties
Superior Marine Corrosion Resistance
Silicon Bronze provides exceptional resistance to corrosion, especially in saltwater environments. Unlike many steels, it does not rust but instead develops a protective blue-green patina over time. This makes it an ideal material for long-term exposure to the elements. Manufacturers produce these fasteners from specific alloys to meet rigorous industry demands.
| Alloy (Common Name) | U.S. Standard |
|---|---|
| C65500 (High-Silicon Bronze A) | ASTM B98 / UNS C65500 |
| C65100 (Low Silicon Bronze A) | ASTM B98 / UNS C65100 |
These standards ensure the material delivers consistent, reliable performance in harsh conditions.
Good Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
This material is an effective conductor of electricity. Its conductivity rating, often around 16% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard), makes it highly suitable for electrical applications. Silicon Bronze 651, in particular, offers superior conductivity compared to other bronze alloys. This property minimizes energy loss and ensures a safe, reliable electrical connection.
Aesthetic Golden-Brown Finish
Silicon Bronze hex head bolts possess a rich, golden-brown color when new. This warm, metallic finish is highly valued in architectural and decorative applications. Over time, the material patinas gracefully, adding character to structures and projects where appearance is a key consideration.
Low Friction Properties
The alloy exhibits low-friction characteristics, which helps prevent galling. Galling is a form of wear caused by adhesion between sliding surfaces, a common problem with stainless steel threads. The low friction of silicon bronze ensures that threaded connections can be assembled and disassembled smoothly without seizing.
Primary 2026 Applications
Marine Construction and Boat Building
The Gold Standard for Marine Fastening ⚓ In traditional and modern boat building, Silicon Bronze bolts are essential. They secure planking, deck hardware, and structural components below the waterline. Reputable manufacturers maintain ISO 9001:2015 certification and perform rigorous salt spray testing per ASTM B117 to guarantee performance.
Electrical Grounding Systems
The combination of high conductivity and corrosion resistance makes Silicon Bronze ideal for electrical grounding. It is used for grounding rods, connectors, and switchgear hardware. The material forms a protective oxide layer that ensures a dependable, long-lasting electrical connection, even in chemically aggressive soil or coastal air.
Architectural Restoration
Architects and builders use Silicon Bronze bolts for restoring historic buildings and creating high-end architectural features. The material’s classic appearance and ability to withstand weathering make it perfect for projects that demand both authenticity and longevity.
Plumbing and Hydraulic Systems
Silicon Bronze fasteners are used in select plumbing and hydraulic systems. Their resistance to corrosion from various fluids and their low-friction properties ensure durable, leak-free connections for pumps, valves, and pipe flanges.
9. Polymer Composites (PEEK)
Polymer composites, led by Polyetheretherketone (PEEK), represent a revolutionary shift away from traditional metal fasteners. This high-performance thermoplastic offers a unique combination of mechanical strength, chemical stability, and low weight. In 2026, engineers increasingly specify PEEK hex head bolts for advanced applications where metals are unsuitable. It provides a robust, non-metallic solution for some of the most demanding technological environments.
Key Properties
Lightweight and Metal-Free
PEEK fasteners are exceptionally lightweight, offering a significant weight reduction compared to steel, titanium, and even aluminum. This metal-free characteristic is crucial for applications that require electrical insulation or transparency to magnetic fields and radio frequencies. The material’s low density helps improve efficiency in weight-sensitive systems.
High Chemical and Hydrolysis Resistance
This polymer exhibits outstanding resistance to a broad spectrum of aggressive chemicals, solvents, and acids. PEEK also resists hydrolysis, meaning it does not degrade when exposed to high-pressure water or steam. This makes it an excellent choice for equipment that undergoes frequent sterilization cycles.
Excellent Strength at High Temperatures
PEEK maintains its excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and stiffness, at elevated temperatures. Its molecular structure provides inherent stability, allowing it to perform reliably under demanding thermal loads.
High-Temperature Performance 🔥 Unreinforced PEEK offers a continuous service temperature of up to 250°C (482°F). Manufacturers can also produce fiber-reinforced grades (using glass or carbon fibers) that exhibit even greater heat resistance and rigidity.
Electrical Insulation
As a polymer, PEEK is an excellent electrical insulator. This property prevents short circuits and electromagnetic interference in sensitive electronic assemblies. Its high dielectric strength makes it an ideal material for securing components in high-voltage applications.
Primary 2026 Applications
Electronics Manufacturing
The electronics industry uses PEEK bolts to fasten components in circuit boards and assembly equipment. Their insulating properties prevent electrical arcing, while their chemical purity ensures they do not contaminate sensitive electronic parts during manufacturing.
Medical Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
PEEK is essential for constructing MRI machines and other medical imaging devices. Its non-metallic nature ensures it does not interfere with the powerful magnetic fields used during scans. Key requirements for these applications include:
- Pure radiolucency, making the fasteners invisible to MRI, CT, and X-ray scanners.
- Biocompatibility for use in devices that may contact patients.
- Resistance to gamma rays used for sterilization.
Semiconductor Industry
The semiconductor fabrication process demands extreme cleanliness and precision. PEEK fasteners meet these stringent requirements, as they do not release particles or gases that could ruin silicon wafers.
- Ultra-high purity with low extractables and outgassing prevents contamination in cleanroom environments.
- High thermal stability and electrical insulation are critical for maintaining precision in fabrication equipment.
Aerospace Components
Engineers in the aerospace sector use PEEK bolts for interior cabin components, electronic enclosures, and sensor mounts. The material’s low weight helps reduce overall aircraft mass, improving fuel efficiency, while its high-temperature resistance ensures reliability.
10. Graphene-Coated Steels
Graphene-coated steels represent the frontier of fastener technology in 2026. This innovative approach does not replace the steel bolt itself but enhances it with a microscopically thin layer of graphene. This single-atom-thick coating of carbon imparts extraordinary properties to conventional steel fasteners. It transforms a standard bolt into a high-performance component capable of withstanding extreme environmental and mechanical challenges.
Key Properties
Unprecedented Corrosion Resistance
A graphene coating creates an exceptionally effective, impermeable barrier on the steel’s surface. This layer is so dense that it physically blocks moisture and corrosive molecules from reaching the metal. Its impermeable nature prevents rusting and chemical damage, dramatically extending the fastener’s lifespan far beyond traditional coatings.
Reduced Friction Coefficient
The atomically smooth surface of graphene significantly lowers the friction coefficient of the bolt’s threads. This property helps prevent galling during installation, especially with stainless steel fasteners. It also allows for more precise and consistent torque application, ensuring a reliable clamping force.
Increased Surface Hardness
Despite its thinness, a graphene layer adds remarkable hardness to the bolt’s surface. This diamond-like hardness protects the fastener from scratches, abrasion, and wear. The result is a bolt that maintains its integrity even in high-contact, dynamic applications.
Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance
High-strength steel bolts can become brittle and fail when exposed to hydrogen. The impermeable graphene coating acts as a robust shield. It prevents hydrogen atoms from penetrating the steel’s metallic structure, effectively mitigating the risk of hydrogen embrittlement and ensuring long-term structural safety.
Primary 2026 Applications
High-Wear Industrial Machinery
Manufacturers use graphene-coated bolts in machinery with constant vibration and moving parts. The coating’s low friction and high hardness reduce wear on both the fastener and the surrounding components, leading to longer service intervals and reduced maintenance costs.
Advanced Automotive Components
The luxury and high-performance automotive sectors utilize these advanced fasteners. While the high production cost of graphene, averaging around $45 per gram in 2024, limits widespread adoption, its benefits justify the expense in high-value applications where corrosion protection and performance are paramount.
Long-Life Infrastructure Projects
Building for the Future 🏗️ For critical infrastructure like bridges and tunnels, longevity is key. Graphene coatings offer a path to 100-year service lives for steel components.
- The coating’s corrosion resistance protects steel from environmental decay.
- It enhances the durability of the entire structure by ensuring fastener integrity.
- It supports sustainable construction by reducing the need for future repairs and material replacement.
While high initial costs are a factor, significant R&D investments, which grew by 15% annually from 2018 to 2023, are steadily making this technology more economically viable for large-scale projects.
Renewable Energy Systems (Wind Turbines)
Offshore wind turbines operate in one of the most corrosive environments on Earth. Graphene-coated hex head bolts provide the ultimate protection against saltwater spray and harsh weather. This superior corrosion resistance is critical for minimizing costly and dangerous maintenance operations on remote, difficult-to-access turbine towers.
The following table provides a quick-reference comparison of the top 10 materials.
| Material | Strength | Corrosion Resistance | Cost | Defining 2026 Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Good to High | Low (Requires Coating) | Low | General Construction |
| Stainless Steel | Good | Excellent | Medium | Food Processing Machinery |
| Alloy Steel | Very High | Low (Requires Coating) | Medium-High | Oil & Gas Sector |
| Titanium Alloys | Very High | Exceptional | Very High | Aerospace Systems |
| Nickel Alloys | High | Superior | Very High | Jet Engines |
| Super Duplex | Very High | Excellent | High | Desalination Plants |
| Aluminum Alloys | High | Good | Medium | Drones (UAVs) |
| Silicon Bronze | Medium | Superior | High | Marine Construction |
| PEEK | Good | Exceptional | Very High | Medical MRI Equipment |
| Graphene-Coated | High | Unprecedented | Highest | Long-Life Infrastructure |
Material selection for hex head bolts in 2026 is a strategic decision. Engineers must balance performance, environment, and cost. Factors like material quality and manufacturing processes influence final pricing. Choosing the right material is critical for ensuring safety, longevity, and efficiency in every advanced engineering application.
FAQ
Why is carbon steel still number one in 2026?
Carbon steel offers an unmatched balance of strength, low cost, and wide availability. Industries rely on its proven performance for general construction and mass manufacturing. Its grade-specific properties allow engineers to select the perfect strength level for countless applications, making it a practical and economical choice.
When should an engineer choose 316 over 304 stainless steel?
Engineers specify 316 stainless steel for environments with high chloride exposure.
Its added molybdenum provides superior resistance to saltwater and corrosive chemicals. This makes 316 the ideal choice for marine equipment and chemical processing plants, while 304 suits less aggressive conditions.
What makes titanium bolts worth their high cost?
Titanium bolts provide exceptional strength at roughly half the weight of steel. This strength-to-weight ratio is critical in aerospace and high-performance racing. Their outstanding corrosion resistance and biocompatibility also justify the cost for advanced medical implants and chemical processing equipment where failure is not an option.
Are PEEK bolts as strong as metal bolts?
PEEK bolts are not as strong as high-grade steel but offer excellent strength for a polymer. Their value comes from other properties:
- They are lightweight and metal-free.
- They provide electrical insulation.
- They resist aggressive chemicals and high temperatures. These traits make them essential for specialized electronics and medical MRI applications.
How does a graphene coating protect a steel bolt? 🛡️
A graphene coating creates an impermeable, single-atom-thick barrier on the steel’s surface. This microscopic layer physically blocks moisture and corrosive molecules. It also increases surface hardness and reduces friction, providing unprecedented protection against rust, wear, and hydrogen embrittlement for long-life applications.







